
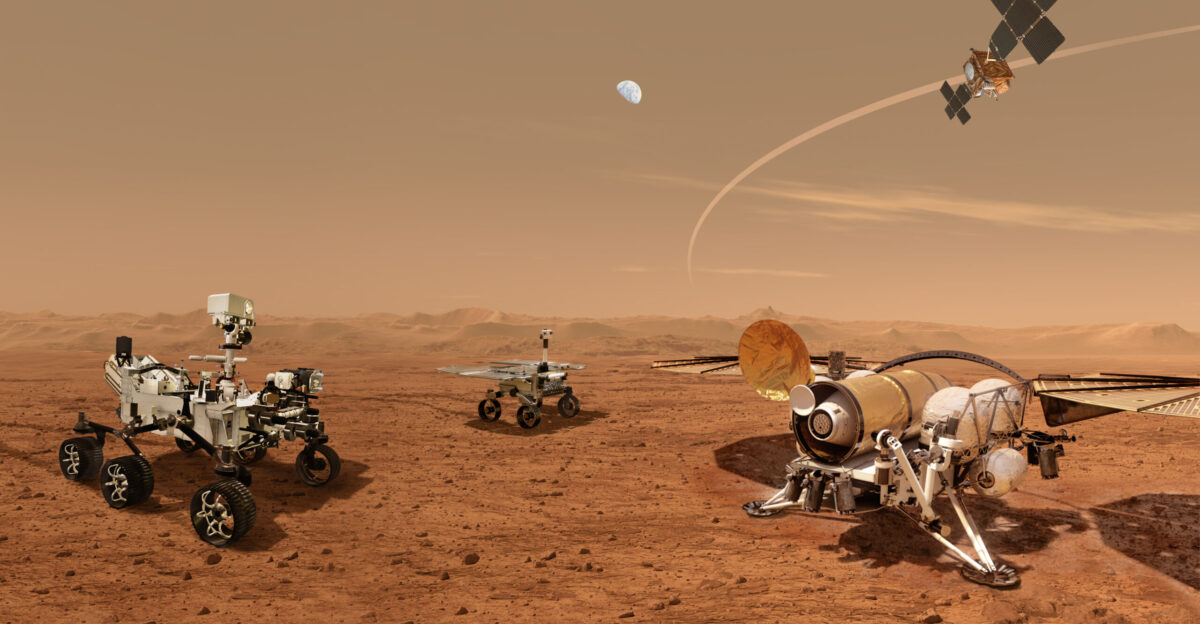
NASA and China are locked in an unprecedented competition to achieve humanity’s first rocket launch from another planet’s surface, with Mars samples worth their weight in scientific gold hanging in the balance. While NASA’s Perseverance rover has collected 33 pristine samples from Mars’ ancient lake bed, bringing them home requires launching the first interplanetary rocket, a feat never attempted in human history. According to NASA’s latest mission updates, the stakes couldn’t be higher as both nations race toward 2028 launch windows.
Mars Sample Return Mission Costs Balloon to Staggering $11 Billion, Forcing Complete Program Overhaul
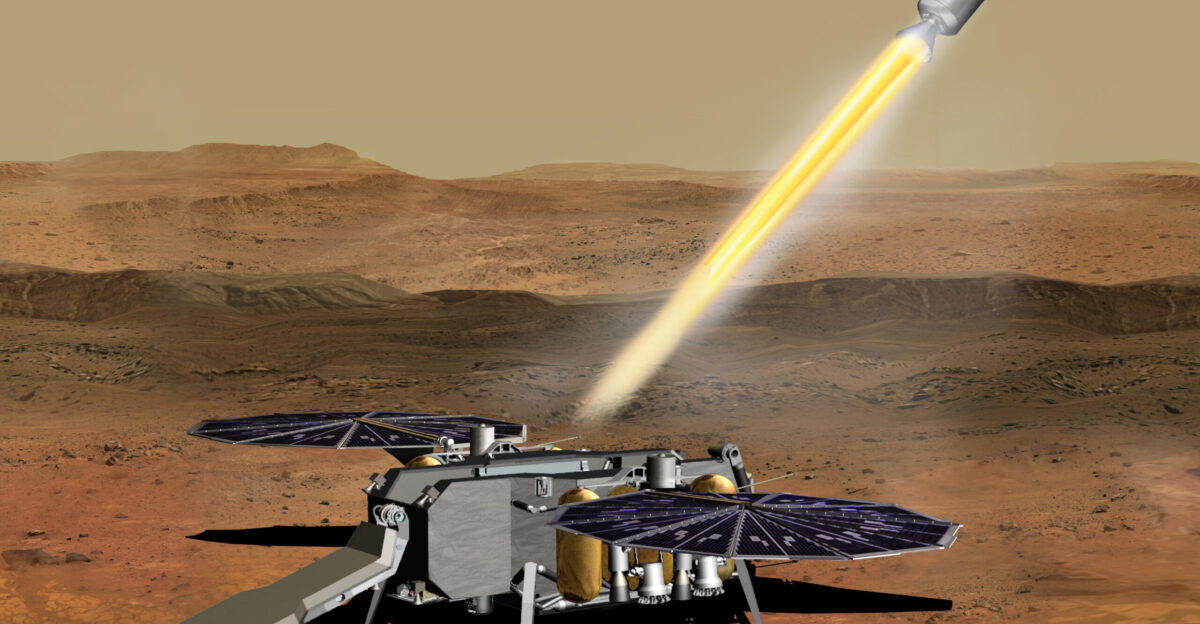

The Mars Sample Return mission has exploded from NASA’s original $3 billion estimate to a jaw-dropping $11 billion price tag, forcing the agency to redesign its approach or risk losing the entire program completely. An independent review board found the costs “unacceptably expensive,” with sample return pushed back to 2040, prompting Administrator Bill Nelson to declare the timeline “unacceptably too long.” Meanwhile, reports indicate from CSIS analysis that China’s Tianwen-3 mission targets a 2031 sample return at a fraction of the cost.
Historic NASA-European Partnership Tackles Most Complex Space Mission Ever Attempted
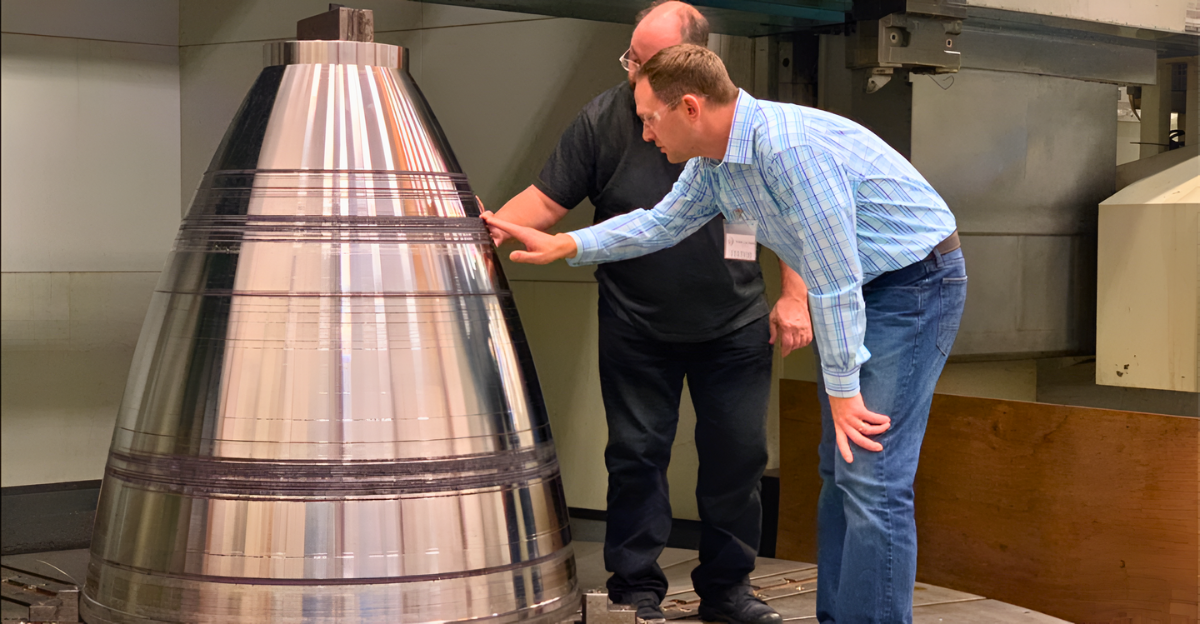
The NASA-ESA Mars Sample Return program represents the most complex international space collaboration ever attempted, requiring unprecedented coordination between American and European space agencies. In March 2021, NASA awarded Northrop Grumman an $84.5 million contract to develop the Mars Ascent Propulsion System, marking the beginning of serious hardware development for humanity’s first interplanetary rocket launch. Government contracts show that the partnership aims to combine NASA’s sample collection expertise with ESA’s orbital return technology.
Engine Tests Prove Mars Rocket Technology Ready for Historic Launch Attempt

Northrop Grumman has successfully completed multiple engine tests for the Mars Ascent Vehicle, validating the two-stage solid rocket motor design that will power the historic first launch from Mars’ surface. The 10-foot-tall rocket underwent rigorous testing at facilities in Maryland, with program manager Jeff Bemis confirming they have “demonstrated a flight-ready design.” Industry publications report that these tests represent crucial milestones in proving the technology needed for the unprecedented Mars surface-to-orbit mission.
First Mars Rocket Successfully Tested on Earth, Clearing Path for Interplanetary Launch
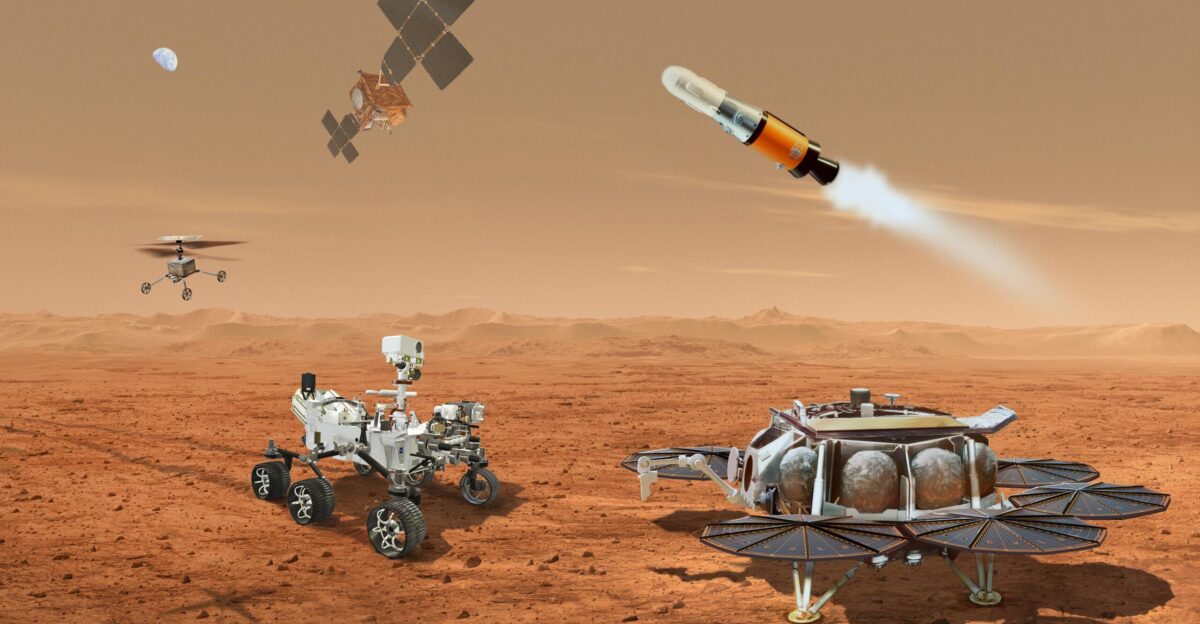

NASA has officially developed and tested the Mars Ascent Vehicle’s propulsion system, marking humanity’s readiness to attempt the first rocket launch from another planet’s surface. The breakthrough came through Northrop Grumman’s successful engine firing tests, validating the solid rocket motor technology that will lift Martian samples from the planet’s surface to orbit for retrieval by a European spacecraft. JPL scientists confirm that this achievement will bring NASA within reach of the historic launch scheduled for late 2020.
Perseverance Creates First Sample Storage Depot on Another World at Mars’ Three Forks Site

Perseverance has established the first sample storage depot on another world at a location dubbed “Three Forks” in Mars’ Jezero Crater, where 10 titanium tubes containing scientifically invaluable samples await future collection. The depot serves as a crucial backup, with samples spread in a zigzag pattern 15 to 50 feet apart to ensure safe retrieval by future missions. This milestone represents tangible progress toward bringing Mars material to Earth for analysis in terrestrial laboratories, NASA imagery confirms.
Scientists Believe Mars Samples May Hold Evidence of Ancient Life Beyond Earth
“We have demonstrated a flight-ready design,” declared Jeff Bemis, Northrop Grumman’s Mars Ascent Vehicle program manager, emphasizing the technical readiness achieved through successful engine testing campaigns. NASA’s Perseverance team has meticulously documented each sample’s geological context, with mission scientists believing they may have collected evidence of ancient microbial life. Research publications suggest that the combination of proven launch technology and scientifically curated samples positions humanity to answer fundamental questions about life beyond Earth.
China’s Tianwen-3 Mission Could Beat NASA to Mars Sample Return by Several Years

China’s Tianwen-3 mission poses a direct competitive threat to NASA’s Mars Sample Return. It plans to launch in 2028 and return over 500 grams of Mars material by 2031—potentially years before NASA’s redesigned mission. The Chinese approach uses a two-launch architecture that combines sample collection and return in a single mission, contrasting with NASA’s multi-mission campaign. Industry experts note China’s track record of meeting announced space mission timelines, including recent lunar sample returns, according to Chinese government announcements.
Mars Sample Return Race Carries Major Implications for Global Space Leadership

The Mars sample return race carries profound implications for global space leadership, with the first nation to achieve this milestone gaining significant scientific and technological prestige. Space policy experts warn that China’s success could demonstrate superior space capabilities and engineering prowess on the international stage. Foreign policy analysts observe that the competition extends beyond science to encompass national security interests and technological supremacy in deep space exploration.
NASA Administrator Pauses Mars Sample Return Due to Unsustainable Cost Overruns

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announced in November 2023 that the Mars Sample Return program was “paused” due to unsustainable costs, forcing a complete mission redesign to find more affordable alternatives. The agency has since solicited industry proposals for alternative architectures, including potential involvement of commercial partners like SpaceX’s Starship or Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket. Space policy documents reveal that this pivot represents a fundamental shift from NASA’s traditional approach to primary science missions.
Aerospace Industry Grows Frustrated with NASA’s Indecision on Mars Mission Direction

Aerospace contractors and space scientists have expressed growing frustration with NASA’s indecision on Mars Sample Return, with multiple design changes and budget constraints creating uncertainty throughout the industry. The Planetary Society and other advocacy groups have criticized the mission’s management, calling for decisive leadership to prevent further delays. Industry sources indicate that program delays have disrupted supplier schedules and threatened to scatter the specialized workforce needed for the mission.
Trump Administration Faces Immediate Decision on Future of Mars Sample Return Program
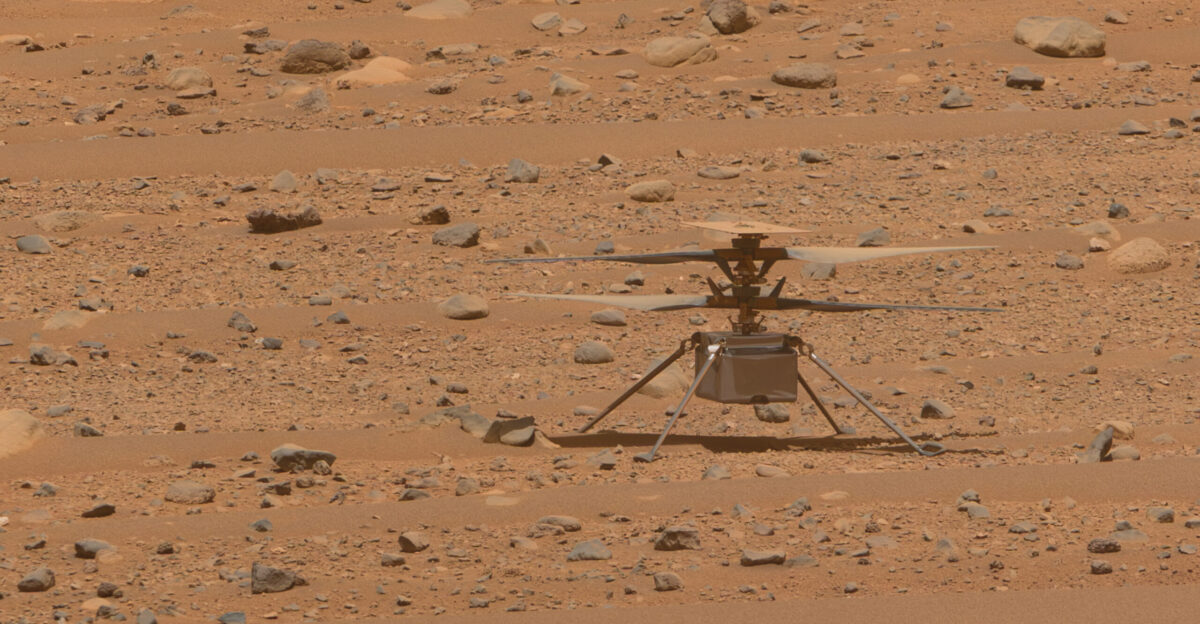

The incoming Trump administration faces an immediate decision on Mars Sample Return’s future, with NASA deliberately leaving the choice of mission architecture to the new leadership team. Administrator Bill Nelson acknowledged that the “responsible thing to do” was providing options rather than forcing a single approach on the new administration. Transition documents show that this transition creates both opportunity and risk for the program’s survival.
NASA Narrows Mars Mission Options to Two Cost-Reduced Architecture Designs
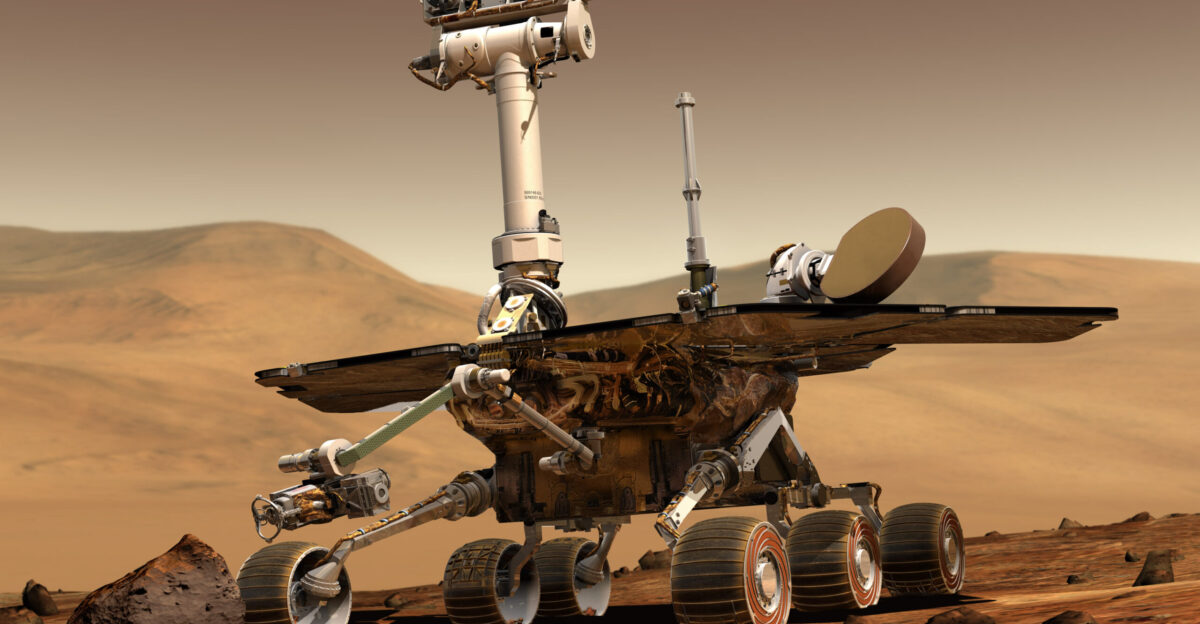

NASA has narrowed Mars Sample Return options to two primary architectures: a modified sky crane approach costing $6.6-7.7 billion, or a commercial heavy lift lander solution costing $5.8-7.1 billion. Both options significantly reduce costs compared to the original $11 billion estimate while potentially enabling sample return by 2035 with adequate funding. The agency selected seven companies, including SpaceX, to study alternative mission designs, procurement records indicate.
Space Experts Question NASA’s Ability to Execute Mars Mission Within Budget Constraints

Independent review boards and space policy experts remain skeptical about NASA’s ability to execute Mars Sample Return within realistic budget constraints, citing the program’s history of cost overruns and technical complexity. Former NASA officials warn that frequent mission redesigns create additional risks and delays that could further jeopardize the program. Policy researchers note that the challenge of maintaining political and financial support across multiple administrations adds uncertainty to long-term mission planning.
Mars Sample Return Success Could Reshape International Space Exploration for Decades
The success or failure of Mars Sample Return will fundamentally reshape international perceptions of American space leadership and technological capabilities in the critical area of deep space exploration. European partners are watching closely as NASA’s struggles could impact future collaborative missions and ESA’s space exploration priorities. ESA officials suggest the outcome will influence decades of future Mars exploration and potential human missions to the Red Planet.
Proposed NASA Budget Cuts Threaten Mars Mission and Broader Planetary Science Programs
The Trump administration’s proposed 24% cut to NASA’s budget threatens Mars Sample Return and the entire planetary science portfolio, forcing difficult prioritization decisions. Congressional space subcommittees demand accountability for cost overruns while balancing support for American space leadership against fiscal constraints. Budget analysts warn that the political dynamics surrounding space exploration funding will determine whether ambitious Mars missions remain viable.
European Space Agency Adapts Mars Program After Losing Russian Partnership Over Ukraine

The European Space Agency has adapted its ExoMars program to launch independently in 2028, replacing Russian partnerships with American launch vehicles and European landing platforms. ESA’s €522 million contract with Thales Alenia Space ensures European Mars exploration continues despite geopolitical tensions and NASA’s uncertainties about the Mars Sample Return. ESA contracts confirm that this demonstrates Europe’s commitment to maintaining independent Mars exploration capabilities.
Private Space Companies Emerge as Potential Game-Changers for Mars Exploration Costs
Private companies like Blue Origin and SpaceX are emerging as potential game-changers for Mars exploration, offering alternative architectures that could reduce costs and accelerate timelines. Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket will launch NASA’s ESCAPADE Mars mission, demonstrating commercial capabilities for interplanetary missions. However, experts question whether commercial solutions meet the stringent planetary protection requirements for sample return missions, as shown by regulatory assessments.
Mars Samples Could Answer Fundamental Questions About Life’s Origins in the Solar System

The Mars samples collected by Perseverance represent potentially the most scientifically valuable extraterrestrial material ever gathered. This has implications for understanding life’s origins and Mars’ habitability throughout solar system history. Advanced laboratory analysis techniques unavailable on Mars could reveal biosignatures or organic compounds, determining whether life existed on Mars. Scientific journals report that the stakes extend beyond individual missions to humanity’s fundamental understanding of life in the universe.
Mars Sample Return Crisis Could Define American Space Leadership for the Next Generation

The Mars Sample Return crisis represents a pivotal moment defining American space leadership for decades. It determines whether the United States remains the world’s premier space exploration nation or cedes leadership to rising competitors. The decisions made in 2025 regarding mission architecture, funding, and international cooperation will echo through future Mars exploration, human missions to the Red Planet, and America’s role in the broader solar system exploration. The first rocket launch from Mars remains humanity’s next giant leap—the question is which nation will take it, strategic analysts conclude.