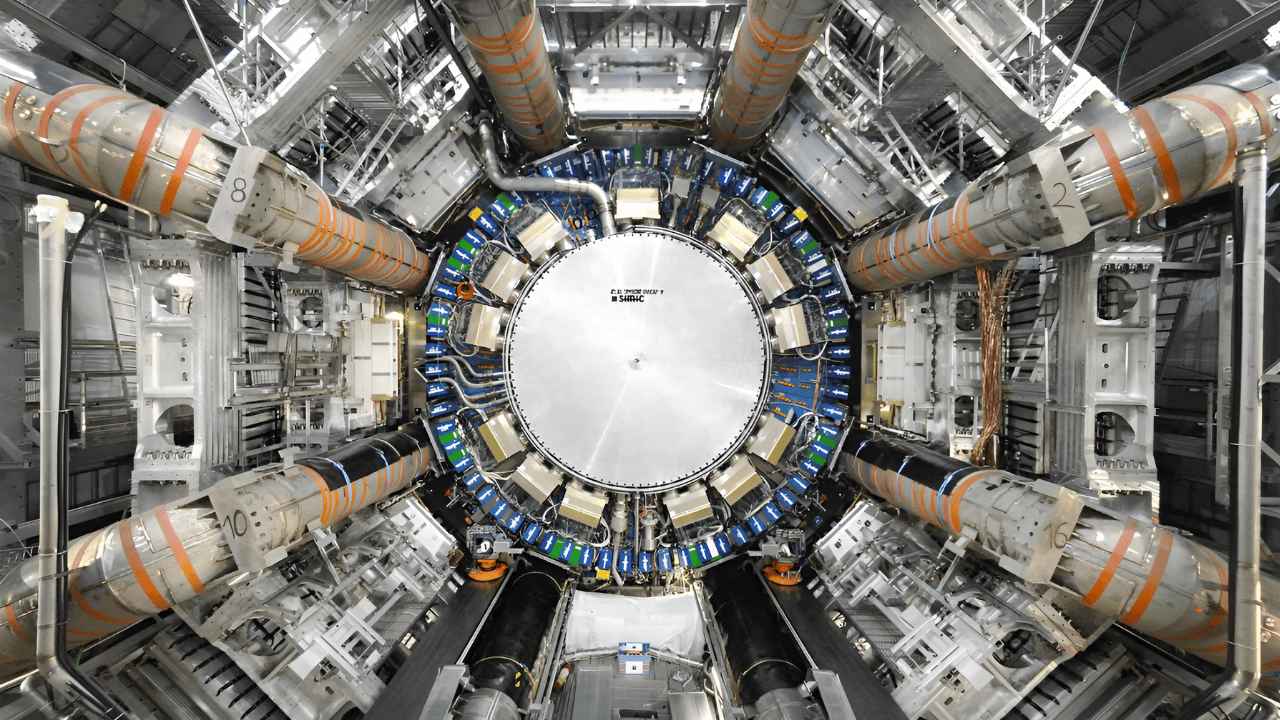
The world’s most powerful particle accelerator has shattered every previous record, marking a pivotal moment for scientific exploration. In 2025, CERN’s Large Hadron Collider (LHC) generated more collision data than any other collider in history, a feat celebrated by physicists and institutions worldwide. The achievement signals a new era in the quest to understand the universe’s deepest mysteries.
A Machine of Unmatched Power

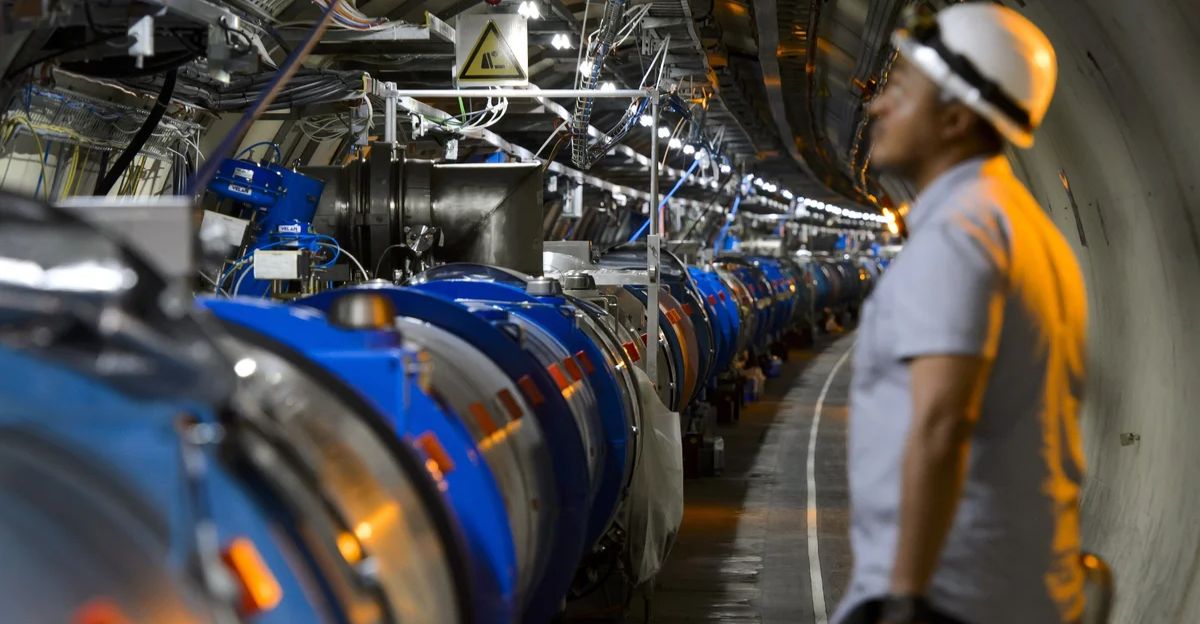
The LHC, a 27-kilometer underground ring near Geneva, Switzerland, is operated by the European Organization for Nuclear Research. Thousands of superconducting magnets propel protons to nearly the speed of light, enabling experiments that probe the fundamental structure of matter. Since its launch in 2010, the LHC has supported researchers from dozens of countries, driving breakthroughs in particle physics and beyond.
Record-Breaking Performance
In 2025, the LHC delivered 125.4 inverse femtobarns of luminosity to its ATLAS and CMS detectors, surpassing its own targets and previous records. Luminosity, a measure of the total particle collisions, is critical for uncovering rare subatomic phenomena. The achievement exceeded the 2024 record by 1.5 inverse femtobarns and outpaced the Tevatron collider’s lifetime output by a factor of ten. Scientists described the milestone as the “gold standard” for collider performance.
A Year of Discovery

On November 4, 2025, CERN scientists celebrated the production of nearly 7 million Higgs bosons—the particle famously dubbed the “God particle”—for the ATLAS and CMS experiments. The figure was calculated from the integrated luminosity and production rates, verified by CERN officials. The unprecedented data volume enables physicists to confirm rare processes, test predictions of the Standard Model, and explore theories beyond it.
Global Impact and Collaboration
The record-setting run is a career highlight for hundreds of scientists and engineers at CERN and partner laboratories. “It’s an emotional moment,” said the LHC Engineer in Charge on the night of the achievement. The success is credited to years of upgrades, meticulous planning, and teamwork, fostering unity across the global scientific community. Researchers from the U.S., China, India, and over thirty other countries collaborate on LHC experiments, broadening participation in analysis and enriching student involvement.
Technological and Scientific Legacy

CERN’s advances regularly benefit the technology sector. Upgrades to the LHC’s beam power and energy storage have improved superconducting materials, medical imaging, and big data processing. The 2025 breakthrough has already inspired next-generation accelerator designs in national laboratories worldwide. The collider’s exceptional performance reinforces the Higgs boson’s status as a cornerstone of modern physics.
Looking Ahead

The 2025 proton run concluded with a carefully controlled “beam dump” into graphite absorbers, safely ending collisions and preparing the facility for its next phase. On November 15, CERN began its heavy-ion program, studying matter under extreme conditions similar to those in the early universe. Researchers are preparing for “Long Shutdown 3” in July 2026, a multi-year pause for upgrades and refurbishments. The flood of high-quality data from 2025 will fuel research for years, with physicists anticipating new discoveries and deeper insights. Regulatory bodies will review the results for compliance with international safety and transparency standards, shaping future upgrades and collaborative policies.
CERN’s record-setting year demonstrates the enduring legacy of the LHC and sets a new benchmark for future projects. The achievements of 2025 represent not just a technical triumph, but a testament to the power of global collaboration in advancing science and technology.